Contents
Takin: A Cohort of Superior Quality Zero-shot Speech Generation Models
DPI-TTS: Directional Patch Interaction for Fast-Converging and Style Temporal Modeling in Text-to-Speech
Additive-feature-attribution methods: a review on explainable artificial intelligence for fluid dynamics and heat transfer
Qwen2-VL: Enhancing Vision-Language Model's Perception of the World at Any Resolution
JEAN: Joint Expression and Audio-guided NeRF-based Talking Face Generation
Denoising diffusion models for high-resolution microscopy image restoration
UKAN: Unbound Kolmogorov-Arnold Network Accompanied with Accelerated Library
Symmetry-Enriched Learning: A Category-Theoretic Framework for Robust Machine Learning Models
Pareto Data Framework: Steps Towards Resource-Efficient Decision Making Using Minimum Viable Data (MVD)
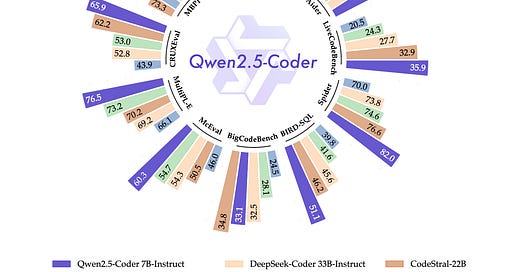
Qwen2.5-Coder Technical Report
To CoT or not to CoT? Chain-of-thought helps mainly on math and symbolic reasoning
A Controlled Study on Long Context Extension and Generalization in LLMs
Creative Beam Search: LLM-as-a-Judge For Improving Response Generation
Improving Ontology Requirements Engineering with OntoChat and Participatory Prompting
Generalized Robot Learning Framework
Takin: A Cohort of Superior Quality Zero-shot Speech Generation Models
Authors: EverestAI, :, Sijin Chen, Yuan Feng, Laipeng He, Tianwei He, Wendi He, Yanni Hu, Bin Lin, Yiting Lin, Pengfei Tan, Chengwei Tian, Chen Wang, Zhicheng Wang, Ruoye Xie, Jingjing Yin, Jianhao Ye, Jixun Yao, Quanlei Yan, Yuguang Yang
Source and references: https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.12139v1
Introduction
This research paper introduces Takin AudioLLM, a series of techniques and models designed for high-quality, zero-shot speech generation and personalized audiobook production. The Takin AudioLLM series includes Takin TTS, Takin VC, and Takin Morphing.
Key Points
Takin TTS is a neural codec language model that can generate high-fidelity, natural-sounding speech in a zero-shot manner.
Takin VC employs a joint modeling approach to enhance speaker similarity and intelligibility, as well as a conditional flow matching-based decoder to improve speech quality and naturalness.
Takin Morphing enables users to customize speech production with their preferred timbre and prosody, leveraging advanced timbre and prosody modeling techniques.
The Takin AudioLLM series aims to drive innovation and support audiobook production by allowing users to tailor speech generation to their specific needs.
Methodology
The Takin AudioLLM series employs a multi-stage training approach, including unsupervised pretraining on multimodal data, supervised fine-tuning for downstream tasks like TTS and ASR, and continual supervised fine-tuning with domain-specific and speaker-specific techniques. The models incorporate neural codecs, language models, and conditional flow-based decoders to achieve high-quality, natural-sounding speech synthesis.
Results and Findings
The researchers report that the Takin AudioLLM series models are capable of generating high-quality, near-human-like speech that is nearly indistinguishable from real human speech. The models demonstrate robustness and effectiveness in complex real-world scenarios, and the Takin Morphing system, in particular, provides a high degree of control over timbre and prosody for personalized audiobook production.
Implications and Conclusions
The Takin AudioLLM series represents a significant advancement in zero-shot speech production technology, addressing the growing demand for personalized audiobook production and enabling users to tailor speech generation to their specific requirements. The research has the potential to significantly enhance user experience and drive further progress in the field of generative speech modeling.
DPI-TTS: Directional Patch Interaction for Fast-Converging and Style Temporal Modeling in Text-to-Speech
Authors: Xin Qi, Ruibo Fu, Zhengqi Wen, Tao Wang, Chunyu Qiang, Jianhua Tao, Chenxing Li, Yi Lu, Shuchen Shi, Zhiyong Wang, Xiaopeng Wang, Yuankun Xie, Yukun Liu, Xuefei Liu, Guanjun Li
Source and references: https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.11835v1
Introduction
This research paper proposes a novel method called Directional Patch Interaction for Text-to-Speech (DPI-TTS) that addresses the limitations of existing Diffusion Transformer (DiT) speech models by incorporating specific acoustic processing.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to State of AI to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.